What Is 720×480 Resolution?
720×480 resolution refers to a display specification where the screen image is made up of 720 horizontal pixels and 480 vertical pixels. This screen resolution is typically associated with standard-definition video (SD) and is commonly used in DVDs, digital TVs, and older gaming consoles. It is also known as SD 480p, where the “p” stands for progressive scanning—a method where all lines of the frame are drawn sequentially, enhancing image stability and clarity compared to older interlaced methods.
Despite its lower pixel count than modern high-definition and ultra-high-definition resolutions, 720×480 remains relevant for certain applications. For example, many digital cameras and streaming equipment still employ this resolution for specific video formats to ensure broader compatibility and lower storage requirements.
Where is 720×480 Resolution Used Today?
While the world increasingly gravitates towards HD and UHD resolutions, 720×480 resolution still holds its ground in several specific applications. Its ease of use, compatibility across various platforms, and lower data requirements make it a practical choice in some scenarios. Here’s where you might encounter 720×480 resolution today:
- DVDs and Legacy Media: Most standard DVDs use the 720×480 resolution, ensuring compatibility with older playback devices.
- Broadcast Television: Some digital TV channels, particularly those transmitting standard-definition content, still operate at this resolution.
- Video Streaming: Lower-resolution streaming to reduce bandwidth usage, particularly for mobile devices on limited data plans.
- Security Cameras: Many surveillance systems utilize 720×480 to balance data storage needs with adequate video quality.
- Video Production: This is used for specific video formats and archival purposes, ensuring they are viewable on a wide range of devices.
Pros and Cons of 720×480 Resolution
Pros
- Widespread Compatibility: The 720×480 resolution aligns with the specifications of standard DVD players and older television sets, ensuring broad compatibility for playback and distribution.
- Smaller File Sizes: Compared to higher resolution formats such as HD or 4K, video content in 720×480 resolution typically results in smaller file sizes, making it practical for storage and distribution on physical media and digital platforms with bandwidth limitations.
Cons
- Limited Visual Clarity: As a standard definition format, 720×480 resolution may lack the visual sharpness and detail present in higher resolution formats, influencing the viewing experience, especially on larger screens and modern displays.
- Less Suitable for Large Screens: When displayed on larger monitors or high-definition screens, the limitations of 720×480 resolution become more apparent, potentially compromising the visual quality and immersion of the content.
The Bottom Line
While it may seem less impressive than today’s high-definition standards, its continued relevance in several niche but significant applications proves its enduring practicality. Whether for DVDs, standard-definition broadcasts, or efficient video streaming, 720×480 offers a balanced mix of quality and compatibility that can’t be ignored.
As high-definition formats continue to dominate the media landscape, understanding the characteristics and implications of 720×480 resolution can aid content creators, video producers, and consumers in navigating the evolving landscape of digital video production and distribution while maintaining compatibility with legacy systems and formats where required.
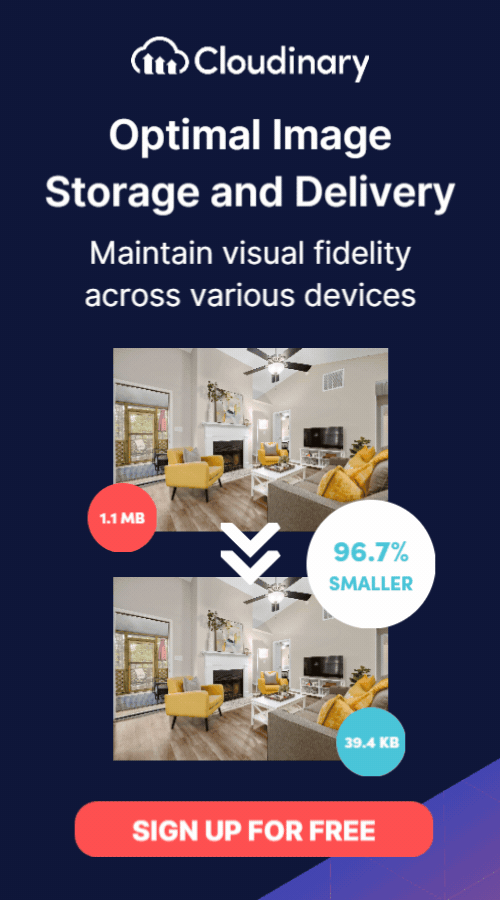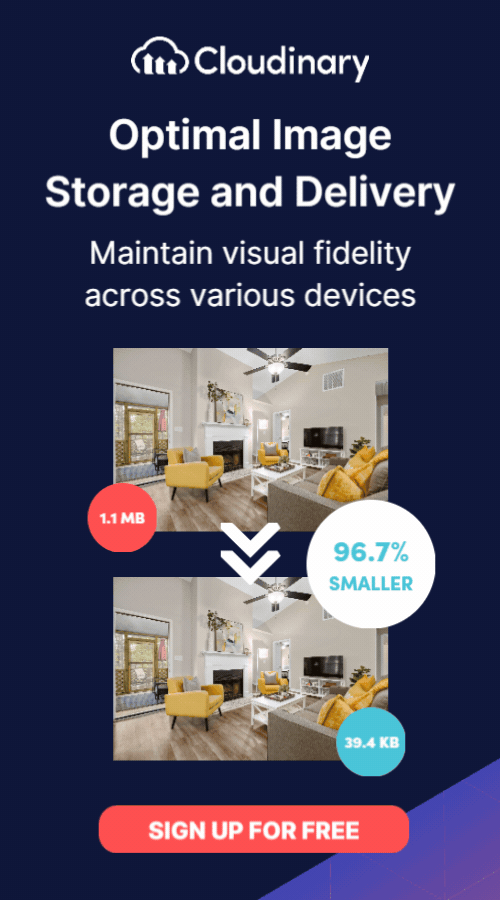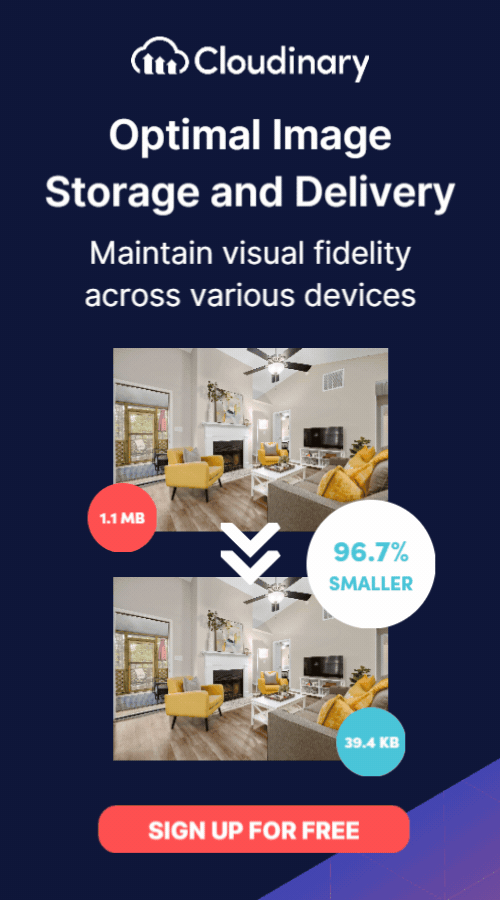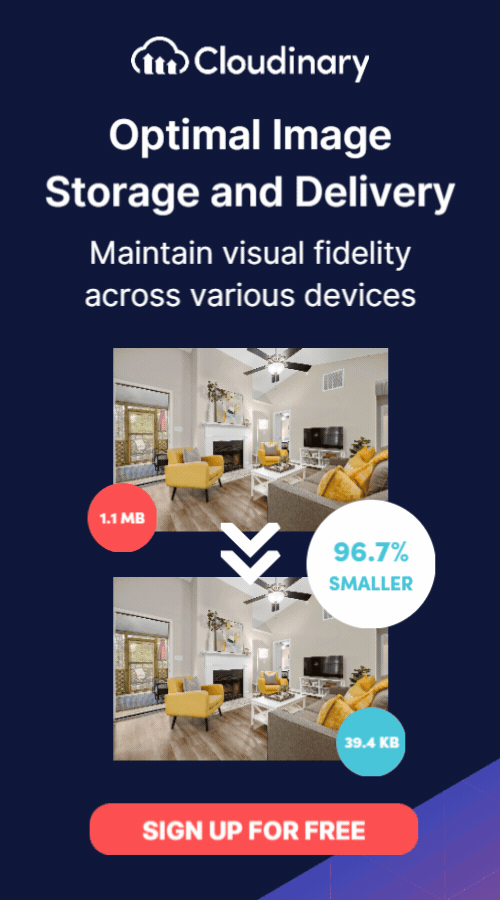
Transform and optimize your images and videos effortlessly with Cloudinary’s cloud-based solutions. Sign up for free today!